- AMD’s Ryzen AI MAX+ 395 “Strix Halo” APU makes significant strides in AI processing for consumer laptops.
- Combines Zen 5 CPU cores, a 50 TOPS XDNA 2 NPU, and an integrated GPU for unparalleled performance.
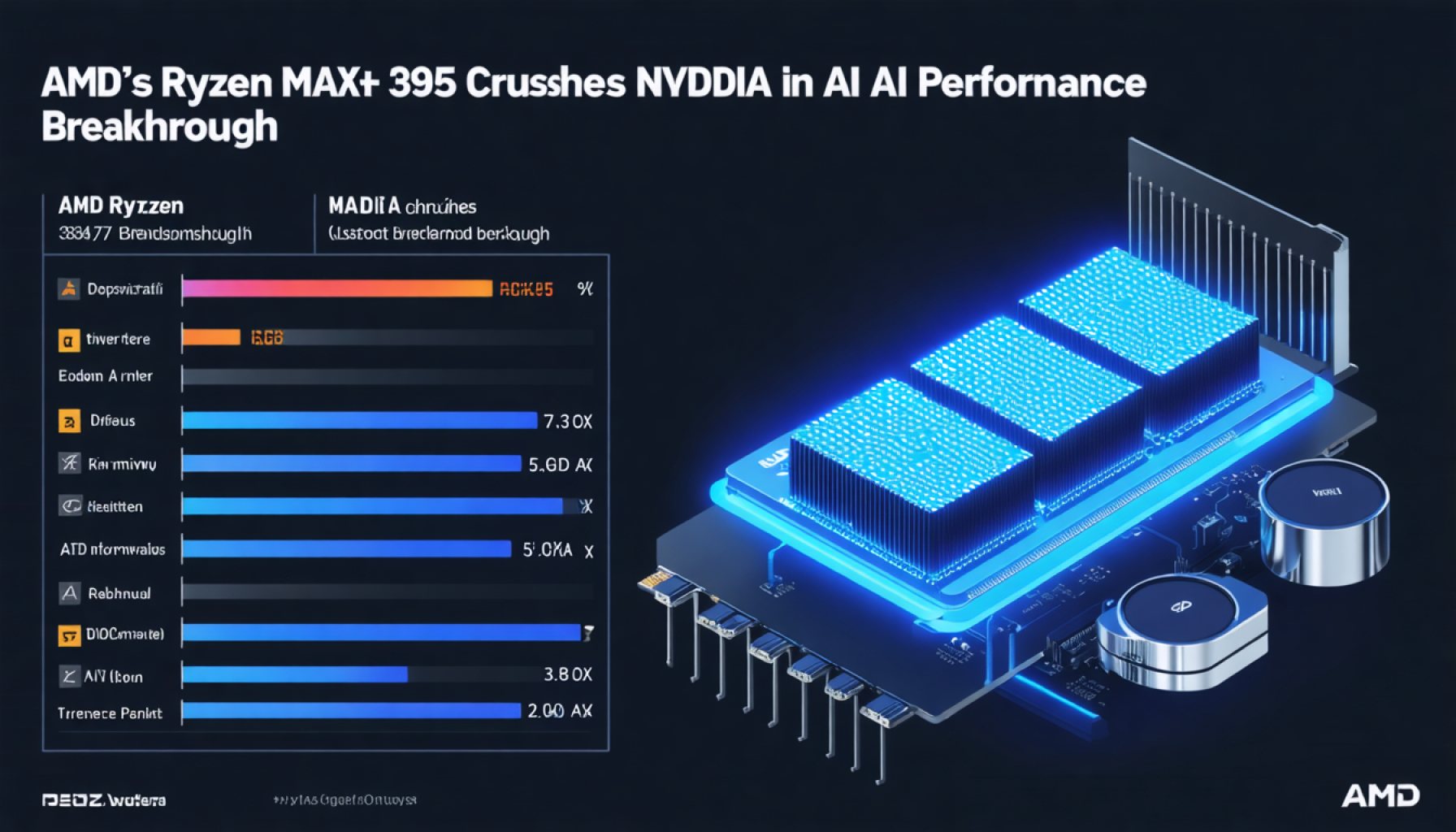
- Surpasses NVIDIA’s RTX 5080 with up to 2.2x faster token throughput and 12.2x speed increases in some models.
- Delivers up to 7x improvement in the performance of vision models.
- Features 128GB total memory, convertible up to 96GB VRAM, enhancing model operation.
- Exceeds traditional VRAM limits, surpassing NVIDIA’s RTX 5080 and RTX 5090.
- Balances energy efficiency and performance, making it ideal for AI applications without reliance on the cloud.
The relentless march of technology sometimes offers a leap so pronounced that it stops us in our tracks and urges us to take notice. The recent unveiling of AMD’s Ryzen AI MAX+ 395 “Strix Halo” APU does just that. This next-generation processor not only outpaces its competition; it redefines what users can expect from AI processing, especially in consumer laptops.
Imagine a processor that combines the agile Zen 5 CPU cores with the sheer power of a 50 TOPS XDNA 2 NPU and an integrated GPU. Together, they orchestrate a performance symphony that sings the future of computing. AMD’s new hero, Ryzen AI MAX+ 395, breathes new life into AI applications, especially as it takes the crown from NVIDIA’s renowned RTX 5080 in the latest benchmarks.
Why is this important? Imagine running complex AI models locally on your machine without breaking a sweat. No longer tethered to extensive cloud infrastructures, users can now savor the freedom of state-of-the-art AI with exceptional ease. Applications like LM Studio are ready to unleash the true potential of this technological marvel, enabling users to dive into the world of intelligent computing without technical acrobatics.
As we delve into the details, the Ryzen AI MAX+ 395 not only surpasses its rivals; it charges ahead with a proficiency that is hard to ignore. Token throughput can exceed what is offered by Intel’s Arc 140V by up to 2.2 times. Smaller models, such as Llama 3.2 3b Instruct, experience a performance boost of up to 4x faster time to the first token, an innovative delight for tasks requiring quick responses. Models with parameters from 7-8B soar with up to an astonishing 9.1x improvement, while 14B parameter models race ahead with 12.2x the speed of Intel Core Ultra 258V.
The APU’s agility extends beyond mere calculations. Vision models, which are the backbone of modern machine learning, are transformed. AMD’s processor offers up to 7x faster performance in IBM Granite Vision 3.2 3b tests and significantly enhances the execution of Google Gemma 3 models, which are 4.6x faster for the 4b variant and 6x faster for the 12b variant.
What drives these advancements is the formidable 128GB total memory, a stark contrast to the modest offerings from competitors. By converting up to 96GB to VRAM via Variable Graphics Memory, AMD enables models like Google Gemma 3’s colossal 27B Vision to operate seamlessly, a feat previously unattainable on other platforms.
Take a moment to imagine the contrasts: AMD’s Strix Halo harnesses the full potential of its large VRAM, soaring above the RTX 5080’s 16GB ceiling. Even NVIDIA’s RTX 5090, with an offering of 32GB, cannot compete with the efficiency and potential energy savings of AMD’s new powerful chip, especially when considering the massive power draws of 360W and 575W from these discrete GPUs.
In situations where model sizes strain VRAM limits, AMD’s solution shines brightly. While NVIDIA’s discrete solutions maintain superiority for specific use scenarios, AMD’s offering remains a robust integrated package that seamlessly blends energy efficiency with uncompromising performance.
The Ryzen AI MAX+ 395 stands as a testament to what is possible at the evolving intersection of AI and everyday computing. It invites a new era where performance barriers dissolve, paving the way for innovation and discovery. This is more than a step forward – it is a giant leap that marks a new dawn in the digital age.
Why AMD’s Ryzen AI MAX+ 395 Transforms AI Processing in Laptops
The launch of AMD’s Ryzen AI MAX+ 395 “Strix Halo” APU marks a transformative moment in AI processing for consumer laptops. This advanced APU integrates Zen 5 CPU cores with a potent 50 TOPS XDNA 2 NPU and a cutting-edge integrated GPU, enabling remarkable performance advancements in AI applications. This article explores the untold facets of this processor, its implications for the industry, and practical advice for potential users.
Key Features and Specifications
1. Zen 5 CPU Cores: AMD’s latest architecture offers significant improvements in processing efficiency and speed compared to previous generations.
2. 50 TOPS XDNA 2 NPU: This neural processing unit delivers an astounding 50 trillion operations per second, making it ideal for AI workloads that require high computational power.
3. Total Memory Architecture: A groundbreaking feature with 128GB total memory, enabling seamless data transfers between CPU and GPU, optimizing performance for intensive tasks.
4. Variable Graphics Memory: With the ability to convert up to 96GB of this total memory to VRAM, it is possible to handle larger and more complex AI models with ease.
Real-World Use Cases
– AI Model Processing: The APU supports running complex AI models locally on laptops, which can replace reliance on cloud processing and offer savings and enhanced privacy.
– Gaming and Graphics: The integration of high-performance graphics capabilities means gamers can experience improved gameplay with reduced latency.
Market Trends and Industry Predictions
– Movement Towards Integrated Systems: As seen with the Ryzen AI MAX+ 395, the industry is moving towards integrated solutions that combine high performance with energy efficiency, reducing the need for large, power-hungry discrete GPUs.
– Increased AI Adoption: With processors like the Ryzen AI MAX+ 395 democratizing access to powerful AI processing, an increase in AI-driven applications and innovations across various sectors is expected.
Comparison with Competitors
– NVIDIA RTX 5080 and 5090: While NVIDIA maintains a strong grip on discrete GPUs, the efficiency and integration of AMD’s APU offer significant advantages for those seeking powerful yet energy-efficient solutions.
– Intel Arc 140V and Core Ultra 258V: In head-to-head benchmarks, AMD’s chip shows a significant lead, particularly in AI tasks, offering up to 12.2x speed improvements.
Advantages and Disadvantages Overview
Advantages:
– Extraordinary AI processing power.
– High efficiency and reduced energy consumption.
– Large memory capacity for handling big models.
Disadvantages:
– May not match the absolute top performance of top-tier discrete GPUs in specialized scenarios.
– The initial cost may be higher due to the groundbreaking technology.
Security and Sustainability
– Energy Efficiency: By integrating such powerful components into a single APU, energy efficiency is prioritized, reducing the environmental impact compared to setups reliant on discrete GPUs.
– Security Enhancements: AMD’s architecture is designed with robust security features to protect data, which is particularly important when processing sensitive information locally.
Tips and Recommendations
– Assess Your Needs: Determine whether your use case benefits from an integrated APU or requires the specific capabilities of a discrete GPU.
– Stay Updated: Keep informed about updates and driver improvements from AMD to ensure your processor operates at its peak level.
For more technological innovations and insights, visit [AMD](https://www.amd.com).
This new processor from AMD reshapes what consumers can expect from AI processing in laptops, making it a compelling choice for tech enthusiasts and professionals. As AI becomes increasingly embedded in everyday computing, technologies like the Ryzen AI MAX+ 395 APU demonstrate significant progress towards a more integrated and efficient future.